Facebook Outreach
Action Module
Training Series # 15
- Introduction
- Getting Started
- Guided Creation
- Ad Types
- Targeting On Facebook
- Finding Targets
- Tips & Tricks
- Conclusion
- Resources
- An Added Note
- Terms and Conditions
Introduction
Unless you’ve been living under a rock for the last decade or so, you already know how huge Facebook is. They claim to have over 1 billion daily active users, and many of those people on average spend close to an hour a day using the site.
The biggest problem with Facebook in recent years is that their organic reach—the people you can reach without spending money—has declined to nearly zero. Even if you have a fan page with thousands of fans, you still have to pay to reach your own fans. Crazy, right?
It’s not all that crazy if you think about it. Most people are fans of dozens, if not hundreds of pages on Facebook. If all those pages shared several articles per day, most of the posts would just get lost. There’s just too much content being posted.
So, Facebook has implemented some changes that make it so that only a small fraction of a page’s followers can ever see each post.
We all know this wasn’t done solely to keep Facebook’s users happy. It has pushed a lot of people to spend money on ads, despite having a huge following on the site. It’s a wonder they don’t have a mutiny on their hands! But since they’re such a huge source of traffic, we all do what we have to do, which is paying for ads even if we already have thousands of fans.
Yes, it just doesn’t sit well for those of us who paid for advertising to obtain those fans in the first place, because we then have to pay again to have our posts reach those fans we already paid for. It’s double-dipping at its finest. Pay attention: “if you wanna play, you gotta pay.” And it’s their site, so it’s their rules.
In this guide, you’re going to learn how to basically beat Facebook at its own game by learning how to create ads that will get both paid and organic reach. Keep reading and you’ll see how to get the most bang for your buck by learning how to create widely successful ads at the lowest prices possible.
You’re going to find out, unlike most Facebook users:
- the best ways to target the right audience for maximum profitability,
- how to keep your costs down, and
- how to use retargeting to pull in potential lost sales.
So, let’s get started!
First, we understand that re-targeting is a new concept to many of you.
We have full tutorials on this subject on our site. Internetvisionsdefined.com
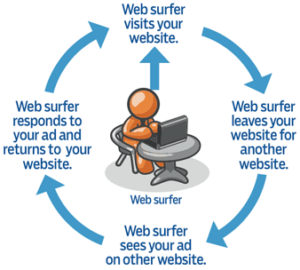
Getting Started
The first thing you need to do is log into your Facebook account, or create one if you don’t already have one. You can use your personal Facebook account for this if you want, because your ads are in no way linked to your name. They’d be linked to your Facebook fan page, if anything.
It is highly recommended that you do all your work with Facebook Ads on a desktop computer or laptop, not on a mobile device. If you don’t have a desktop or laptop, see if you can borrow one, or use one at a library or internet café. The dashboard is buggy at times on mobile.
For the more adventurous there are a couple of options for mobile:
1. The “clunky” way: click on the menu at the bottom right, and scroll down in the “explore” section to Ads Manager, or a bit more user friendly way,
2. The “recommended” way from the App store download the Facebook Ads app.
It’s much more “user friendly.” 
From your desktop to get to your dashboard, click the small arrow at the top right of your Facebook profile to bring up the drop-down menu and click on either “Create Ads” or “Manage Ads”.
You can also just type in the URL if you can’t find this option easily:
>> http://www.facebook.com/ads
If you’re using an ad blocker, they’ll ask you to turn it off or add the web page to your exception list. Once this is done, you should refresh the page. (How to Refresh a Page: On Windows, Press the F5 key
On Mac, Hold Command and Press R)
You may find this dashboard a little confusing at first. There are a lot of available options, and sometimes they can seem a little redundant. The same information may appear in multiple locations. Take a little time to get familiar with the dashboard before jumping into ad creation.
You’ll notice there’s a Guided Creation mode that will help guide you through the process and a Quick Creation mode for people who are a little more familiar with the Facebook Ads creation process.
Once you’ve got a hang of the basic options, take a close look at the different types of ads that are currently available.
Guided Creation
If you’re new to Facebook Ads, try out their Guided Creation mode.
In this mode, you’ll have three different categories of options (Awareness, Consideration, and Conversion) and multiple selections within each category.
Under Awareness, you will see Brand awareness and Reach. Brand awareness is basically when you want to target people as tightly as possible for the best conversion rates, and Reach is when you want to get as many views or visitors as possible.
Most of the time, Brand awareness is the better option, because most businesses want to focus tightly on their niche.
Under Consideration, you will see six different options:
Traffic, Engagement, App installs, Video views, Lead generation and Messages.
Traffic is used to drive traffic to a particular destination. Engagement is to help increase elements such as likes and shares of your content on Facebook. App installs will help you get more people to install your app. Video views will get more people to view your video content. Lead generation will help you build your list, and Messages will help you get more direct messages sent to your Facebook page.
Under Conversion, there are three options:
Conversions, Catalog sales, and store visits.
Conversions will help you get various types of actions on your website or app, such as opting in to your email list, signing up for a membership, or watching a view. Catalog sales will display various products from your online store to increase sales. And Store visits will drive foot traffic to a brick-and-mortar location.
Confused, yet? Don’t worry, keep reading.
Let’s say you have an online store selling pet supplies. You want to get more people to buy your products, so you should choose “Catalog sales”. This allows you to add items from your online store to a catalog of merchandise that let you make different types of ads that focus on selling specific items.
In order to use this type of ad, you’ll need to set up your catalog. There are four types of catalogs you can create: E-commerce, Travel, Real Estate, and Auto. The other three categories are self-explanatory, and the E-commerce category covers anything that doesn’t fit into those three (anything sold online.)
If you’re using Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, Magento, or Google to sell your products, they have a process that will help you import your entire product catalog quickly. If you’re using the E-commerce category for your catalog, you can save a lot of time with this method.
Each selection has a specific purpose, so you can choose the one that’s right for your goals.
Once you’ve decided which type of campaign you’d like to run, it’s time to start targeting your audience.

Ad Types
Once you get used to creating Facebook Ads, you might switch over to manual creation. This will make everything a little easier to customize, but it can be a bit daunting for new marketers.
There are many different types of ads, but almost all of them will require some sort of image or video. Right now, let’s cover some different types of ads that you’re most likely to create right now.
1. Link click ads are the most popular type of ad. They can send people to your website, blog, landing page, squeeze page, etc. These ads can be placed in the right column, desktop newsfeed, mobile newsfeed, audience network, or on Instagram.
The recommended size is 1,200 x 628 pixels, 90 characters of ad copy, a 25-character headline, and 30 characters for the description.
2. Video ads are also very popular on Facebook. These can only be placed on the desktop newsfeed, mobile newsfeed, audience network and on Instagram.
Videos should be in either 16:9 or 9:16 ratio, up to 4 GB in file size, and no longer than 120 minutes in length. (The best performing videos are 15-30 seconds.) Your ad copy can be up to 90 characters.
3. Boosted page posts will help you get more views, likes, comments, and shares of posts on your Facebook page.
You can target your own Facebook page audience, or others based on your targeting. They can appear on the desktop newsfeed, mobile newsfeed, audience network and Instagram.
The recommended image size is 1,200 x 628 pixels, with unlimited ad copy text, a 25-character headline, and a 30-character link description.
A boosted page post will look just like the original post, but it will have “Sponsored” at the top.
4. Carousel ads are great for selling multiple products, so if you have an online store or if you sell many different products, it can be a great way to showcase a few to a single user in one post. They can appear on the desktop newsfeed, mobile newsfeed, audience network and Instagram.
Recommended image size is 1080 x 1080 or 600×600. Ad copy is 90 characters, 25-character headline, and 30-character link description.
5. Lead ads are perfect for building your email list. They can appear on the desktop newsfeed, mobile newsfeed, audience network and Instagram.
Recommended image size is 1,200 x 628. Ad copy is 90 characters, 25- character headline. 30-character link description.
6. The context card can either be in paragraph format with unlimited text, or as a 5-bulletpoint list with 80 characters per point.
The context card headline can be up to 60 characters, with 30 characters for the button. You must include a privacy policy and link to your website.
7. Canvas ads are a newer development and have several major benefits. Because of their nature, they can only be shown on the mobile newsfeed, but they are remarkably effective. They allow users to swipe through a carousel of images, tilt the image, and zoom in or out.
These ads load up to 10 times faster than most mobile applications, so they’re great at grabbing attention!
The recommended image size is 1,200 x 628. Ad copy should be under 90 characters. Headline should be under 45 characters. And there are many different components you can include in a canvas ad, including header with logo, full-screen image, text block, image carousel, auto-play video, and many more.
Play around with different options until you find one that converts well for you.
8. Page like ads will help you get more likes to your page, but it’s important to keep in mind that this is probably not the best use of your marketing dollars if you’re looking for pure ROI.
Remember, have a huge page on Facebook isn’t worth as much as it used to be, because organic reach is next to zero these days. This means you’ll have to pay for the same traffic twice, because you’ll have to pay once to obtain the fans, and again to be able to reach those fans.
That’s not to say page likes aren’t valuable. If someone is a fan of your page, it usually means they are at least somewhat interested in what you have to offer.
This makes targeting your other ads a little easier. Just keep in mind that page like ads should be considered a part of your overall, long-term marketing strategy, and not a short-term source of traffic and sales.
Page like ads can be shown in the right column, desktop newsfeed and mobile newsfeed. Choosing the right image is crucial, so be sure to test a few different ones to find the most effective.
9. Page post photo ads are meant for increasing engagement on your fan page. If you choose the right photo, you’ll get a lot of comments, likes, and shares.
You can even drop a link into the description, but you aren’t likely to get too much traffic to it. This type of post is meant primarily to increase engagement.
Page post photo ads can be shown in the right column, desktop newsfeed and mobile newsfeed.
There are lots of other options, as well, but the others are meant for very specific purposes such as getting people to an event or getting people to install an app. You can explore all of the other ad options if any of them apply to you.
Targeting On Facebook
There are hundreds of targeting options on Facebook, and they’re adding more all the time.
You can target by basic demographics such as location, languages spoken, education, where they live, their politics, religion, relationship status, age, and occupation, but also by deeper methods such as hobbies, entertainment, business industries, and more.
Plus, there are advanced targeting methods such as lookalike audiences that will let you target an extremely specific group of people, and website traffic that will target to people have recently visited your website.
If you already have an existing user base of some sort—such as an email list, phone number database, etc.—you can import it into Facebook and let them match the data to as many of their user profiles as possible. This will help you target people you have already done business with or connected with in the past.
Lookalike audiences are also great if you have existing users or traffic, because you can not only target people who have visited your website or subscribed to your email list—but also to profiles that are extremely similar to those people.
This extends your reach beyond your own network, but still allows for fairly tight targeting.
You can also target by location, so if you have a brick-and-mortar location, or if you know your product appeals to people in specific areas more than others, you can narrow down that way.
For example, if you’re selling products specifically for German citizens who have moved to other countries, you’d want to target just those countries that have a high German immigrant population, and NOT Germany itself.
Or if you are selling a class on speaking Spanish for French speakers, you’d wanted to target France, and perhaps the French-speaking areas of Canada or other countries, but not Spain or Mexico.
This can even be used to exclude certain areas, which can be helpful if you get a lot of fraud from a certain location, or if you know the traffic from certain places converts terribly for you.
You can target by age and gender, but unless you’re absolutely certain of your demographics, you might want to leave these open.
For example, you might be targeting women’s lingerie ads to females, and later discover that males tend to buy more of your lingerie for their partners (or themselves) than women do for themselves. In that case, you’d have missed out on a lot of traffic and sales.
You can let the targeting work its magic and find target users without focusing on age or gender.
You can target by the languages they speak, which is very helpful if your material is in a specific language, or if you’re marketing language services.
Finally, there’s more detailed targeting. Here, you can target things such as interests, behaviors, and more. You can target by education level, field of study, ethnic background, housing status, interests, hobbies, what they buy, what they read, and so much more.
It’s a good idea to really go through all of the targeting options available and look for those that might fit your target demographic.
For example, if you are selling pet supplies, you would want to target pet owners, and you might also want to target people who like Cat Fancy or Dog Fancy magazine, people who like the American Kennel Club, and people who like PetSmart.
If you’re selling cars, you might want to target people who bought their car more than three years ago, as they would probably be the most likely to buy a car. You might also want to target young people (under 25) who have never bought a car before.
Remember this handy little motto that you can use to figure out who you should be targeting:
“THIS person would do this, but no one else would.”
For example, your target audience member would read Cat Fancy magazine, but no one else would. (Meaning, no one except someone who really likes cats would be likely to read it.)
It’s critical to know as much as possible about your target demographic, so take every opportunity you can to learn more about them.
Finding Targets
It can be tough to figure out exactly what type of interests and pages to target if you’re not extremely well-versed in your niche. Let’s say you’re targeting the golf niche, but you’re not a big golfer yourself.
You’d obviously target fans of the PGA Tour, and probably some of the big golf club brands, and, of course, a few of the biggest names in golf from yesterday and today, but who else?
You’ll need to dig deeper, because you want to target only the most die-hard fans of golf in order to keep conversions attractive.
Assume you target Tiger Woods. How many of his fans are die-hard fans of golf? Probably quite a few, but there are probably also people who follow him only because he’s a big name, or follow him because of the scandal he was involved in. They may not even be interested in the game of golf itself, just the individual.
So, it’s a good idea to drill down as far as you can. Remember that motto:
“THIS person would do this, but no one else would.”
Research your niche as thoroughly as possible. Then you can find out in what topics the people in your target niche would be interested, but no one else would.
Let’s say you want to target and sell to people who own parrots:
Have all your research done and ready to send to your prospects all for free.
free parrot images
parrot training videos
images of parrots to color
parrot training books
green parrot images
images of parrot fish
cartoon images of parrots
images of parrots in paintings.
Tips & Tricks
Here are a few tips and tricks that will help you take your Facebook Ads marketing to the next level.
- Be sure to use text on your images, but remember to keep it under 20% of the total image.
- Don’t try to lump all your demographics into a single ad unless you know your typical buyers are extremely similar. Assume that you run a store selling movies. People who like action movies might not always like romance movies, so it’s a good idea to create multiple ads to appeal to each specific genre. Then you can change or kill any campaigns that aren’t getting a solid CTR or ROI.
- Stick with the desktop newsfeed placement option initially. It’s the most effective in almost every scenario, and has a decent average cost per click. The biggest exception is when you’re specifically targeting mobile users. In that case, use the mobile newsfeed placement.
- Test out multiple ad formats and then stick with the few that perform best for you. Try out stuff like carousel ads, canvas ads, and video ads if they make sense for your business. You never know what might perform best.
- Use lots of bright colors in your images and videos to grab attention. Try not to blend in with Facebook too much!
- If you’re having any sales or special events, be sure to mention that in your ads, but don’t forget to put a time limit on the ad if your specials will expire. No one likes to click an ad only to find out the deal is expired!
- Include a strong call-to-action in every ad. Want people to opt in to your email list? Tell them! Want them to buy? Tell them! A strong call-to-action can mean the different between stellar results and no results.
- Don’t focus so much on CTR that you lose sight of ROI. Spending too much time trying to optimize your CTR may save you some money on your ads, but if the results harm your ROI, you will lose money in the long run.

Conclusion
Facebook has been one of the biggest sources of traffic online for many years, but recently its organic reach has declined to the point where it’s almost necessary to pay for ads if you want any significant traffic from the site.
This isn’t always a bad thing. Without so much organic clutter from pages, ads are more effective than ever. They are noticed easier, because there’s less content to sift through.
Fortunately, Facebook Ads can be remarkably affordable if you take the time to choose the right ad type for your needs and optimize your campaigns properly. It’s important to test different options and try to find the best combination for your needs.
Take the time to familiarize yourself with all of the various options available in the ad creation dashboard. You’ll want to closely study targeting and placement, as these options can have a huge effect on the success of your campaign.
Remember to stick with the desktop newsfeed placement in the beginning unless you are specifically targeting mobile users. You’ll save a lot of money this way. You can always branch out later.
This concludes our guide on Facebook Ads. I hope you enjoyed it.
Good luck with your campaigns!
Resources
The greatest resource you can find is at internetvisionsdefined.com, both in our tutorial section and in the forum section.
We suggest you read and re-read the action module so you have a full understanding of the ad process.
Beginning in 2108, Facebook has severely limited the reach you can achieve with your fans and followers, and we expect this trend to continue.

An Added Note Concerning Facebook
Some, in March of 2018, are saying that a social media sites, such as Facebook and Google, are public utilities. They may be considered to be an essential public service and should be regulated by the government just as electric utilities are regulated.
These sites are becoming involved in controversies around “fake news,” involving their role in moderating content, their influence in elections, and the personal data they might be able to trade for ads.
Terms and Conditions
Copyright © All rights reserved worldwide.
YOUR RIGHTS: This book is restricted to your personal use only. It does not come with any other rights.
LEGAL DISCLAIMER: This book is protected by international copyright law and may not be copied, reproduced, given away, or used to create derivative works without the publisher’s expressed permission. The publisher retains full copyrights to this book.
InternetVisionsDefined.com has made every reasonable effort to be as accurate and complete as possible in the creation of this book and to ensure that the information provided is free from errors; however, the author/publisher/ reseller assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or contrary interpretation of the subject matter herein and does not warrant or represent at any time that the contents within are accurate due to the rapidly changing nature of the Internet.
Any perceived slights of specific persons, peoples, or organizations are unintentional.
The purpose of this book is to educate and there are no guarantees of income, sales or results implied. The publisher/author/reseller can therefore not be held accountable for any poor results you may attain when implementing the techniques or when following any guidelines set out for you in this book.
Any product, website, and company names mentioned in this report are the trademarks or copyright properties of their respective owners. The author/publisher/reseller are not associated or affiliated with them in any way. Nor does the referred product, website, and company names sponsor, endorse, or approve this product.
COMPENSATION DISCLOSURE: Unless otherwise expressly stated, you should assume that the links contained in this book may be affiliate links and either the author/publisher/reseller will earn commission if you click on them and buy the product/service mentioned in this book. However, the author/publisher/reseller disclaim any liability that may result from your involvement with any such websites/products. You should perform due diligence before buying mentioned products or services.
This constitutes the entire license agreement. Any disputes or terms not discussed in this agreement are at the sole discretion of the publisher.
